Tag
#java
Red Hat Security Advisory 2024-1487-03 - An update for firefox is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.0 Extended Update Support. Issues addressed include integer overflow, out of bounds write, and use-after-free vulnerabilities.
Mozilla released an update of Firefox to fix two critical security vulnerabilities that together allowed an attacker to escape the sandbox.
By Uzair Amir With the increasing popularity of Apache Kafka as a distributed streaming platform, ensuring its high availability has become… This is a post from HackRead.com Read the original post: Best Practices for Kafka Management to Ensure High Availability
### Summary The `email` field in phpMyFAQ's user control panel page is vulnerable to stored XSS attacks due to the inadequacy of PHP's `FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL` function, which only validates the email format, not its content. This vulnerability enables an attacker to execute arbitrary client-side JavaScript within the context of another user's phpMyFAQ session. ### Details Despite using PHP's `FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL` function, the email field does not adequately validate the content of the email address. This means that malicious input, such as JavaScript code, can be accepted and stored in the database without being detected. When the stored data is retrieved and displayed on web pages, it is not properly sanitized to remove or neutralize any potentially harmful content, such as JavaScript code which leads to Stored XSS. ### PoC 1. Login as any user, go to the user control panel, change email to any valid email and intercept the request. 2. Modify the request’s email parameter to t...
### Summary By manipulating the news parameter in a POST request, an attacker can inject malicious JavaScript code. Upon browsing to the compromised news page, the XSS payload triggers. ### PoC 1. Edit a FAQ news, intercept the request and modify the `news` parameter in the POST body with the following payload: `%3cscript%3ealert('xssContent')%3c%2fscript%3e` 2. Browse to the particular news page and the XSS should pop up. 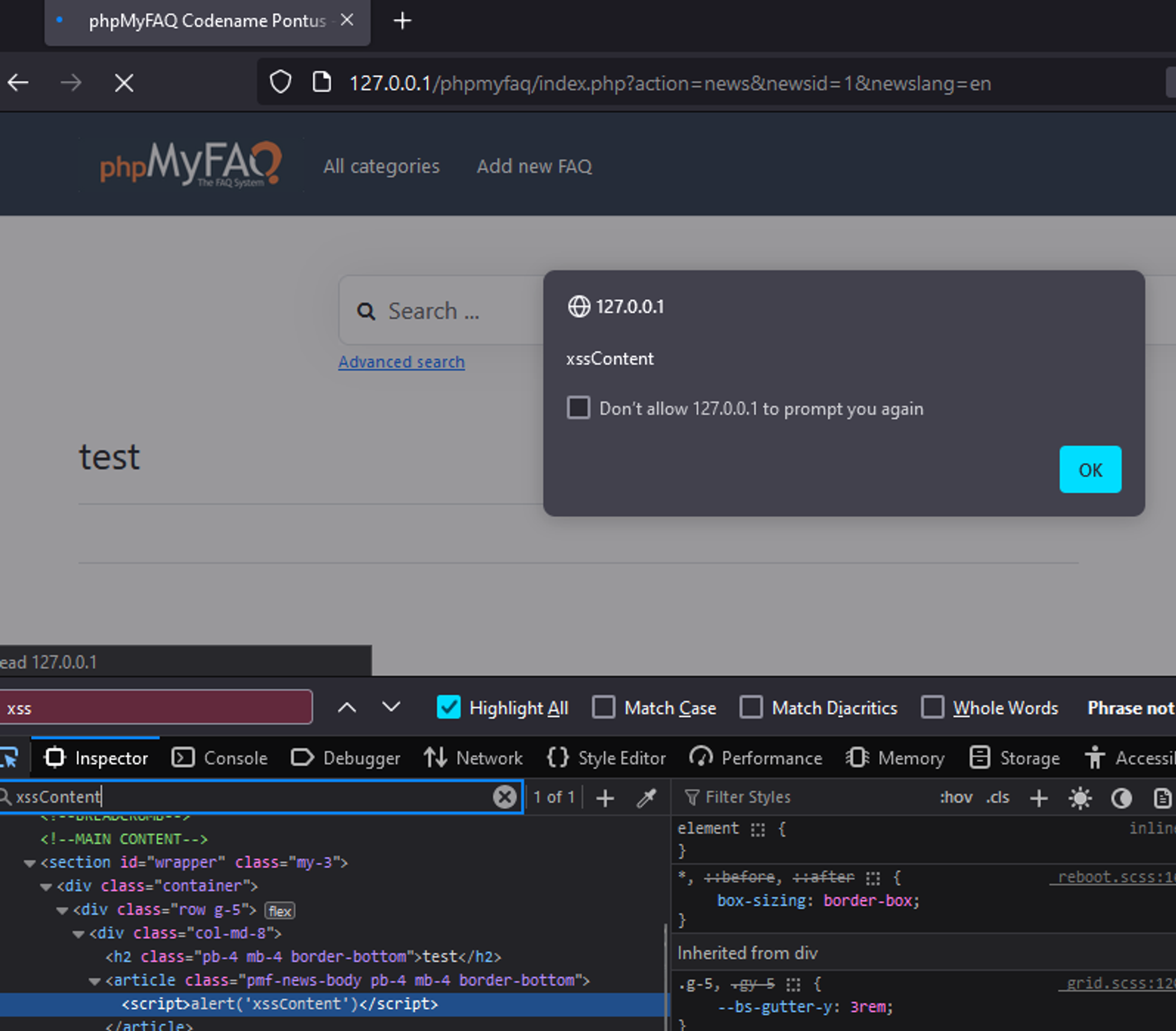 ### Impact This allows an attacker to execute arbitrary client side JavaScript within the context of another user's phpMyFAQ session
### Summary An attacker with admin privileges can upload an attachment containing JS code without extension and the application will render it as HTML which allows for XSS attacks. ### Details When attachments are uploaded without an extension, the application renders it as HTML by default. Therefore allowing attackers to upload .html files containing javascript code to perform XSS attacks. The direct file path to the uploaded attachment is also easily obtainable as it is made up of substrings of the file's MD5 hashes. ### PoC 1. Admin users can upload attachments containing XSS payloads in files without extensions to bypass the .html extension check. 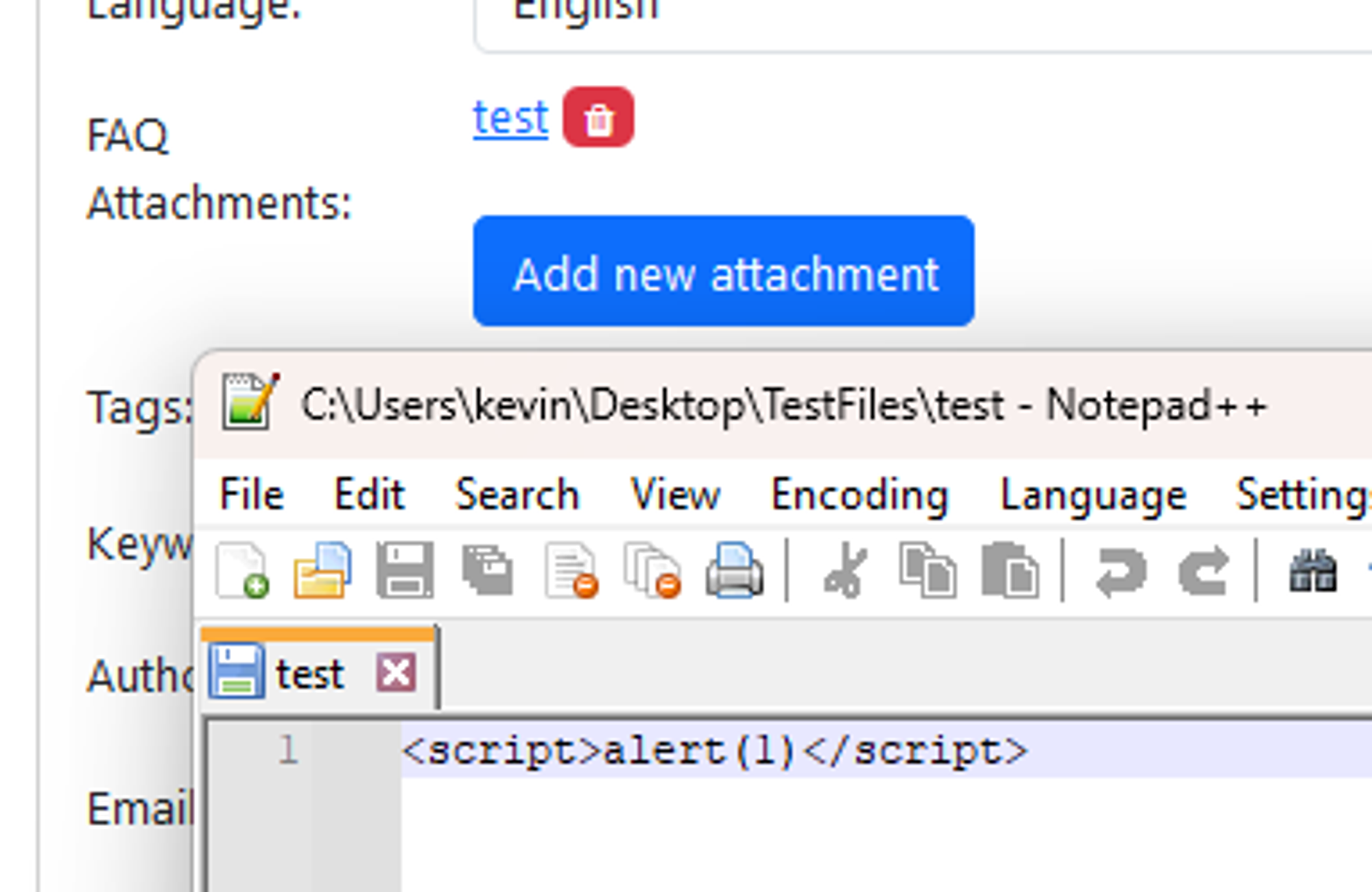 2. Since the path of the uploaded file is built entirely on the file’s MD5 hash and the attachment directory, it is possible for an attacker to know the direct path of the uploaded file. E.g file MD5 hash: 38fff51cb7248a06d6142c6bdf84...
### Summary The `HttpPostRequestDecoder` can be tricked to accumulate data. I have spotted currently two attack vectors ### Details 1. While the decoder can store items on the disk if configured so, there are no limits to the number of fields the form can have, an attacher can send a chunked post consisting of many small fields that will be accumulated in the `bodyListHttpData` list. 2. The decoder cumulates bytes in the `undecodedChunk` buffer until it can decode a field, this field can cumulate data without limits ### PoC Here is a Netty branch that provides a fix + tests : https://github.com/vietj/netty/tree/post-request-decoder Here is a reproducer with Vert.x (which uses this decoder) https://gist.github.com/vietj/f558b8ea81ec6505f1e9a6ca283c9ae3 ### Impact Any Netty based HTTP server that uses the `HttpPostRequestDecoder` to decode a form.
### Impact Code that uses KaTeX's `trust` option, specifically that provides a function to block-list certain URL protocols, can be fooled by URLs in malicious inputs that use uppercase characters in the protocol. In particular, this can allow for malicious input to generate `javascript:` links in the output, even if the `trust` function tries to forbid this protocol via `trust: (context) => context.protocol !== 'javascript'`. ### Patches Upgrade to KaTeX v0.16.10 to remove this vulnerability. ### Workarounds * Allow-list instead of block protocols in your `trust` function. * Manually lowercase `context.protocol` via `context.protocol.toLowerCase()` before attempting to check for certain protocols. * Avoid use of or turn off the `trust` option. ### Details KaTeX did not normalize the `protocol` entry of the `context` object provided to a user-specified `trust`-function, so it could be a mix of lowercase and/or uppercase letters. It is generally better to allow-list by protocol, i...
### Impact KaTeX users who render untrusted mathematical expressions could encounter malicious input using `\includegraphics` that runs arbitrary JavaScript, or generate invalid HTML. ### Patches Upgrade to KaTeX v0.16.10 to remove this vulnerability. ### Workarounds * Avoid use of or turn off the `trust` option, or set it to forbid `\includegraphics` commands. * Forbid inputs containing the substring `"\\includegraphics"`. * Sanitize HTML output from KaTeX. ### Details `\includegraphics` did not properly quote its filename argument, allowing it to generate invalid or malicious HTML that runs scripts. ### For more information If you have any questions or comments about this advisory: * Open an issue or security advisory in the [KaTeX repository](https://github.com/KaTeX/KaTeX/) * Email us at [email protected]
A flaw was found in XNIO. The XNIO NotifierState that can cause a Stack Overflow Exception when the chain of notifier states becomes problematically large can lead to uncontrolled resource management and a possible denial of service (DoS). Version 3.8.14.Final is expected to contain a fix.