Headline
CVE-2022-25165: CVE-2022-25165: Privilege Escalation to SYSTEM in AWS VPN Client - Rhino Security Labs
An issue was discovered in Amazon AWS VPN Client 2.0.0. A TOCTOU race condition exists during the validation of VPN configuration files. This allows parameters outside of the AWS VPN Client allow list to be injected into the configuration file prior to the AWS VPN Client service (running as SYSTEM) processing the file. Dangerous arguments can be injected by a low-level user such as log, which allows an arbitrary destination to be specified for writing log files. This leads to an arbitrary file write as SYSTEM with partial control over the files content. This can be abused to cause an elevation of privilege or denial of service.
Vulnerabilities Overview
Affected Product
The AWS VPN Client application is affected by an arbitrary file write as SYSTEM, which can lead to privilege escalation and an information disclosure vulnerability that allows the user’s Net-NTLMv2 hash to be leaked via a UNC path in a VPN configuration file. These vulnerabilities are confirmed to affect version 2.0.0 and have been fixed in version 3.0.0.
To fix the vulnerabilities, upgrade to version 3.0.0 which can be downloaded here.
Vendor: Amazon Web Service (AWS)
Product: AWS VPN Client (Windows)
Confirmed Vulnerable Version: 2.0.0Fixed Version: 3.0.0
CVE-2022-25166: Arbitrary File Write as SYSTEM
A race condition exists during the validation of OpenVPN configuration files. This allows OpenVPN configuration directives outside of the AWS VPN Client allowed OpenVPN directives list to be injected into the configuration file prior to the AWS VPN Client service, which runs as SYSTEM, processing the file. Dangerous arguments can be injected by a low-level user such as “log”, which allows an arbitrary destination to be specified for writing log files.
The impact is an arbitrary file write as SYSTEM with partial control over the contents of the file. This can lead to local privilege escalation or denial of service.
CVE-2022-25165: Information Disclosure via UNC Path
It is possible to include a UNC path in the OpenVPN configuration file when referencing file paths for directives (such as “auth-user-pass”). When this file is imported to the AWS VPN Client and the client attempts to validate the file path, it performs an open operation on the path and leaks the user’s Net-NTLMv2 hash to an external server.
The impact is information leakage of a user’s Net-NTLMv2 hash. This could be exploited by having a user attempt to import a malicious VPN configuration file into the AWS VPN Client.
What Is AWS VPN Client
AWS VPN Client is a desktop application that can be used to connect to the AWS Client VPN.
From the product website:
The client for AWS Client VPN is provided free of charge. You can connect your computer directly to AWS Client VPN for an end-to-end VPN experience. The software client is compatible with all features of AWS Client VPN.
Arbitrary File Write as SYSTEM Technical Details
AWS VPN Client installs a Windows service which runs as SYSTEM acting as a wrapper to a custom OpenVPN client executable. A low privileged user can use the AWS VPN Client to attempt to connect to a VPN using an imported OpenVPN configuration file.
There are known dangerous OpenVPN directives which perform actions such as running commands or writing log files to a specific destination during a VPN connection. AWS VPN Client attempts to restrict the OpenVPN directives which can be used in the configuration file, but the check fails as it is performed prior to the execution of the OpenVPN executable. This makes it possible to race the execution of the OpenVPN executable after the configuration file has been validated and inject disallowed directives into the file.
Below you can see a log file produced by the AWS VPN service which shows the time between the successful validation of the configuration and the execution of the OpenVPN client.
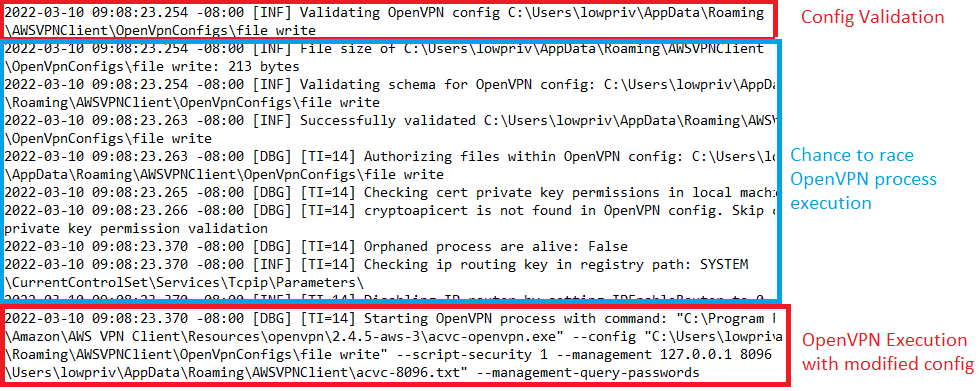
It is easy enough to use a Powershell script to then monitor the log file and upon successful validation of the configuration file immediately write the malicious directive to the configuration file prior to the OpenVPN executable processing it.
With the ability to inject disallowed directives it would seem as easy as adding one of the directives which allows executing a command into the configuration file giving an easy path to privilege escalation. Although in this case it was not this straightforward as AWS VPN service starts the OpenVPN executable with the “–script-security 1” flag, which prevents external binaries or scripts from being executed.
Although we cannot directly run commands, it is still possible to use the “log” directive to redirect log output to any path or file of our choosing. Since execution is done as the SYSTEM user this gives us a privileged file write where we partially control the content. In the simplest case this could be used to write a batch script to an administrator’s startup directory.
A proof of concept for CVE-2022-25166 can be found on our Github repo here.
Information Disclosure via UNC Path Technical Details
AWS VPN Client performs validation on configuration files which are imported into the client as a VPN profile. One of the validation steps consists of checking if a file path exists when any file paths are supplied to directives which accept a file path as an argument.
Some examples of valid directives that accept files paths are
- auth-user-pass
- ca
Validation by AWS VPN Client is done by performing a file open operation on the path to ensure it exists.

AWSVPNClient.Core.dll contains OvpnConfigParser.cs which has the “CheckFilePath” method used to check if a file path is valid. This simply calls File.Open on the supplied file name.
This can be exploited by providing a file that contains UNC paths as the file path. When the file is validated before being imported it will open the UNC path and send the user’s Net-NTLMv2 hash to an external server.
A proof of concept for CVE-2022-25165 can be found on our Github repo here.
Conclusion
Disclosure Timeline
Similar to the Pritunl CVE and blog post recently released, this vulnerability demonstrates the exploit potential in high-privilege Windows processes — such as those used by VPN clients. This also shows how common application flaws are still present in sensitive applications, whether from open source providers or major tech companies.
Stay tuned for another VPN release in the coming weeks!
2/15/2022
Vulnerabilities reported to AWS
2/16/2022
Acknowledged by AWS
3/4/2022
AWS confirmed the issues have been addressed in version 3.0.0
4/12/2022
Full Disclosure (blog post) released
Related news
An issue in upload.csp of FANTEC GmbH MWiD25-DS Firmware v2.000.030 allows attackers to write files and reset the user passwords without having a valid session cookie.
A vulnerability has been discovered in Moxa MGate which allows an attacker to perform a man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack on the device. This affects MGate MB3170 Series Firmware Version 4.2 or lower. and MGate MB3270 Series Firmware Version 4.2 or lower. and MGate MB3280 Series Firmware Version 4.1 or lower. and MGate MB3480 Series Firmware Version 3.2 or lower.
LDAP Account Manager (LAM) is an open source web frontend for managing entries stored in an LDAP directory. The profile editor tool has an edit profile functionality, the parameters on this page are not properly sanitized and hence leads to stored XSS attacks. An authenticated user can store XSS payloads in the profiles, which gets triggered when any other user try to access the edit profile page. The pdf editor tool has an edit pdf profile functionality, the logoFile parameter in it is not properly sanitized and an user can enter relative paths like ../../../../../../../../../../../../../usr/share/icons/hicolor/48x48/apps/gvim.png via tools like burpsuite. Later when a pdf is exported using the edited profile the pdf icon has the image on that path(if image is present). Both issues require an attacker to be able to login to LAM admin interface. The issue is fixed in version 7.9.1.
Nyron 1.0 is affected by a SQL injection vulnerability through Nyron/Library/Catalog/winlibsrch.aspx. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must inject '"> on the thes1 parameter.
A denial of service vulnerability exists in the parseNormalModeParameters functionality of MZ Automation GmbH libiec61850 1.5.0. A specially-crafted series of network requests can lead to denial of service. An attacker can send a sequence of malformed iec61850 messages to trigger this vulnerability.
Multiple cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in Liferay Portal 7.3.5 through 7.4.0, and Liferay DXP 7.3 before service pack 3 allow remote attackers to inject arbitrary web script or HTML via a form field's help text to (1) Forms module's form builder, or (2) App Builder module's object form view's form builder.
stb_image.h v2.27 was discovered to contain an heap-based use-after-free via the function stbi__jpeg_huff_decode.
Irzip v0.640 was discovered to contain a heap memory corruption via the component lrzip.c:initialise_control.
stb_image.h v2.27 was discovered to contain an integer overflow via the function stbi__jpeg_decode_block_prog_dc. This vulnerability allows attackers to cause a Denial of Service (DoS) via unspecified vectors.
SuiteCRM v7.11.23 was discovered to allow remote code execution via a crafted payload injected into the FirstName text field.
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is Attack Complexity marked as High for this vulnerability?** Successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an attacker to take additional actions prior to exploitation to prepare the target environment.
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
**Why is this Chrome CVE included in the Security Update Guide?** The vulnerability assigned to this CVE is in Chromium Open Source Software (OSS) which is consumed by Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based). It is being documented in the Security Update Guide to announce that the latest version of Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) is no longer vulnerable. Please see Security Update Guide Supports CVEs Assigned by Industry Partners for more information. **How can I see the version of the browser?** 1. In your Microsoft Edge browser, click on the 3 dots (...) on the very right-hand side of the window 2. Click on **Help and Feedback** 3. Click on **About Microsoft Edge**
The Signal app before 5.34 for iOS allows URI spoofing via RTLO injection. It incorrectly renders RTLO encoded URLs beginning with a non-breaking space, when there is a hash character in the URL. This technique allows a remote unauthenticated attacker to send legitimate looking links, appearing to be any website URL, by abusing the non-http/non-https automatic rendering of URLs. An attacker can spoof, for example, example.com, and masquerade any URL with a malicious destination. An attacker requires a subdomain such as gepj, txt, fdp, or xcod, which would appear backwards as jpeg, txt, pdf, and docx respectively.
Discourse is an open source platform for community discussion. A category's group permissions settings can be viewed by anyone that has access to the category. As a result, a normal user is able to see whether a group has read/write permissions in the category even though the information should only be available to the users that can manage a category. This issue is patched in the latest stable, beta and tests-passed versions of Discourse. There are no workarounds for this problem.
GeoWebCache is a tile caching server implemented in Java. The GeoWebCache disk quota mechanism can perform an unchecked JNDI lookup, which in turn can be used to perform class deserialization and result in arbitrary code execution. While in GeoWebCache the JNDI strings are provided via local configuration file, in GeoServer a user interface is provided to perform the same, that can be accessed remotely, and requires admin-level login to be used. These lookup are unrestricted in scope and can lead to code execution. The lookups are going to be restricted in GeoWebCache 1.21.0, 1.20.2, 1.19.3.
Discourse is an open source platform for community discussion. In affected versions an attacker can poison the cache for anonymous (i.e. not logged in) users, such that the users are shown the crawler view of the site instead of the HTML page. This can lead to a partial denial-of-service. This issue is patched in the latest stable, beta and tests-passed versions of Discourse. There are no known workarounds for this issue.
Metabase is an open source business intelligence and analytics application. SQLite has an FDW-like feature called `ATTACH DATABASE`, which allows connecting multiple SQLite databases via the initial connection. If the attacker has SQL permissions to at least one SQLite database, then it can attach this database to a second database, and then it can query across all the tables. To be able to do that the attacker also needs to know the file path to the second database. Users are advised to upgrade as soon as possible. If you're unable to upgrade, you can modify your SQLIte connection strings to contain the url argument `?limit_attached=0`, which will disallow making connections to other SQLite databases. Only users making use of SQLite are affected.
An out-of-bounds read/write vulnerability was found in e2fsprogs 1.46.5. This issue leads to a segmentation fault and possibly arbitrary code execution via a specially crafted filesystem.
Two heap-based buffer overflow vulnerabilities exist in the TIFF parser functionality of Accusoft ImageGear 19.10. A specially-crafted file can lead to a heap buffer overflow. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger these vulnerabilities. Placeholder
An authentication bypass vulnerability exists in the Web Application functionality of Moxa MXView Series 3.2.4. A specially-crafted HTTP request can lead to unauthorized access. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Web Application functionality of Moxa MXView Series 3.2.4. Network sniffing can lead to a disclosure of sensitive information. An attacker can sniff network traffic to exploit this vulnerability.
An out-of-bounds write vulnerability exists in the parse_raster_data functionality of Accusoft ImageGear 19.10. A specially-crafted malformed file can lead to memory corruption. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability.
A denial of service vulnerability exists in the cgiserver.cgi Upgrade API functionality of Reolink RLC-410W v3.0.0.136_20121102. A specially-crafted HTTP request can lead to a reboot. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
An SQL injection vulnerability exists in the EchoAssets.aspx functionality of Lansweeper lansweeper 9.1.20.2. A specially-crafted HTTP request can cause SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
A SQL injection vulnerability exists in the HelpdeskEmailActions.aspx functionality of Lansweeper lansweeper 9.1.20.2. A specially-crafted HTTP request can cause SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in the IOCTL GetProcessCommand and B_03 of Webroot Secure Anywhere 21.4. A specially-crafted executable can lead to denial of service. An attacker can issue an ioctl to trigger this vulnerability. An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in the IOCTL GetProcessCommand and B_03 of Webroot Secure Anywhere 21.4. An IOCTL_B03 request with specific invalid data causes a similar issue in the device driver WRCore_x64. An attacker can issue an ioctl to trigger this vulnerability.
An out-of-bounds write vulnerability exists in the OTA update task functionality of Sealevel Systems, Inc. SeaConnect 370W v1.3.34. A specially-crafted MQTT payload can lead to denial of service. An attacker can perform a man-in-the-middle attack to trigger this vulnerability.
A stored cross-site scripting vulnerability exists in the WebUserActions.aspx functionality of Lansweeper lansweeper 9.1.20.2. A specially-crafted HTTP request can lead to arbitrary Javascript code injection. An attacker can send an HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
An authentication bypass vulnerability exists in the device password generation functionality of Swift Sensors Gateway SG3-1010. A specially-crafted network request can lead to remote code execution. An attacker can send a sequence of requests to trigger this vulnerability.
An SQL injection vulnerability exists in the AssetActions.aspx functionality of Lansweeper lansweeper 9.1.20.2. A specially-crafted HTTP request can cause SQL injection. An attacker can make an authenticated HTTP request to trigger this vulnerability.
An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in the RS-274X aperture macro outline primitive functionality of Gerbv 2.7.0 and dev (commit b5f1eacd) and the forked version of Gerbv (commit d7f42a9a). A specially-crafted Gerber file can lead to information disclosure. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability.
An out-of-bounds read vulnerability exists in the RS-274X aperture macro multiple outline primitives functionality of Gerbv 2.7.0 and dev (commit b5f1eacd), and Gerbv forked 2.7.1 and 2.8.0. A specially-crafted Gerber file can lead to information disclosure. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability.
Lack of Neutralization of Formula Elements in the CSV API of MantisBT before 2.25.3 allows an unprivileged attacker to execute code or gain access to information when a user opens the csv_export.php generated CSV file in Excel.
A heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability exists in the sphere.c start_read() functionality of Sound Exchange libsox 14.4.2 and master commit 42b3557e. A specially-crafted file can lead to a heap buffer overflow. An attacker can provide a malicious file to trigger this vulnerability.
A blind SQL injection vulnerability in the ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) extension of MA prior to 5.7.6 can be exploited by an authenticated administrator on ePO to perform arbitrary SQL queries in the back-end database, potentially leading to command execution on the server.
An XSS issue was discovered in COINS Construction Cloud 11.12. Due to insufficient neutralization of user input in the description of a task, it is possible to store malicious JavaScript code in the task description. This is later executed when it is reflected back to the user.
MariaDB Server v10.9 and below was discovered to contain a segmentation fault via the component sql/item_subselect.cc.
MariaDB Server v10.9 and below was discovered to contain a segmentation fault via the component sql/sql_window.cc.
MariaDB Server v10.6.3 and below was discovered to contain an use-after-free in the component my_wildcmp_8bit_impl at /strings/ctype-simple.c.
MariaDB Server v10.9 and below was discovered to contain a segmentation fault via the component sql/item_cmpfunc.cc.
MariaDB Server v10.6.3 and below was discovered to contain an use-after-free in the component VDec::VDec at /sql/sql_type.cc.
Sourcecodester Messaging Web Application 1.0 is vulnerable to stored XSS. If a sender inserts valid scripts into the chat, the script will be executed on the receiver chat.
** UNSUPPORTED WHEN ASSIGNED ** A heap-based buffer overflow exists in XML Decompression DecodeTreeBlock in AT&T Labs Xmill 0.7. A crafted input file can lead to remote code execution. This is not the same as any of: CVE-2021-21810, CVE-2021-21811, CVE-2021-21812, CVE-2021-21815, CVE-2021-21825, CVE-2021-21826, CVE-2021-21828, CVE-2021-21829, or CVE-2021-21830. NOTE: This vulnerability only affects products that are no longer supported by the maintainer.